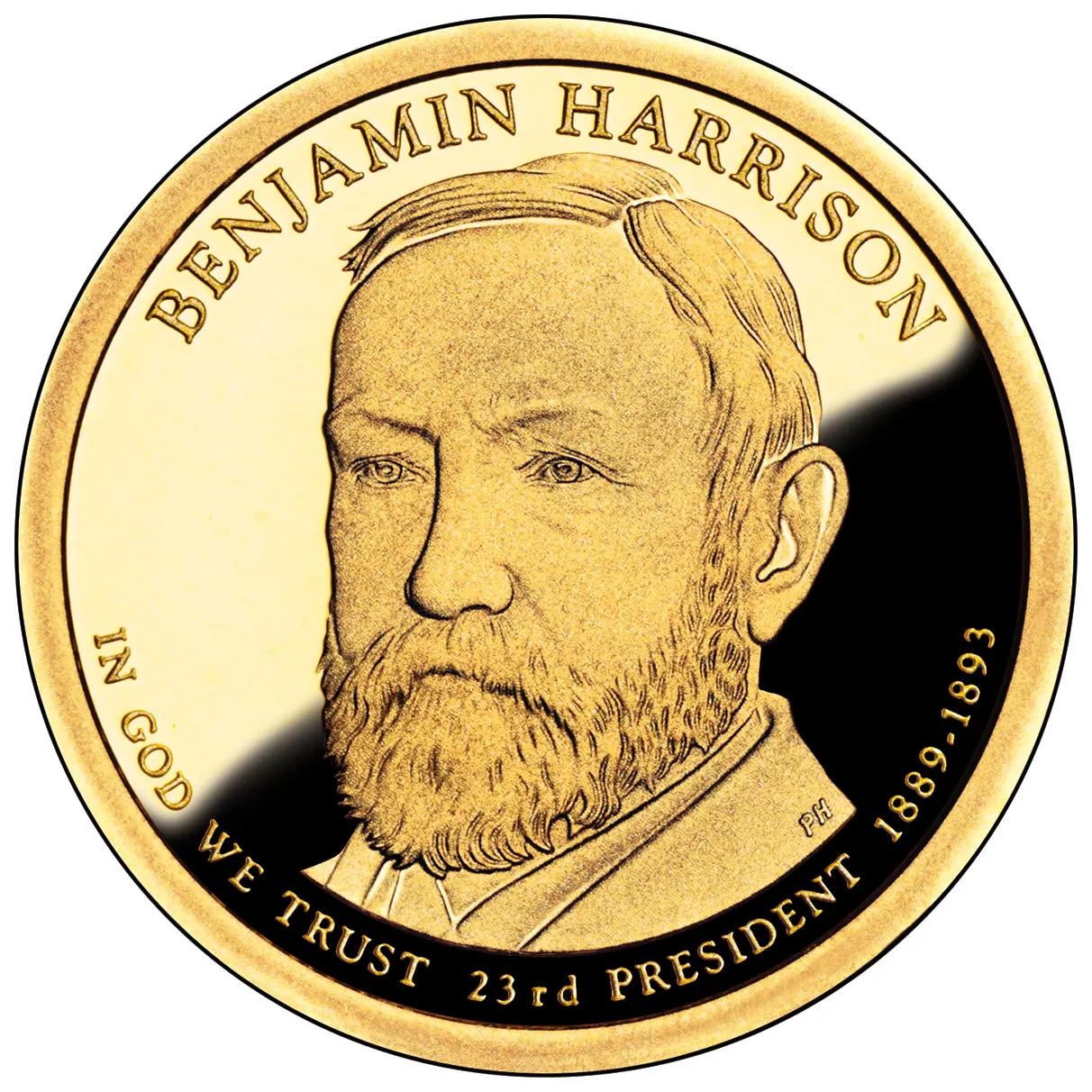
Grandson of former President William Henry Harrison, Benjamin Harrison was born in 1833 on a farm by the Ohio River below Cincinnati. He attended Miami University in Ohio and studied law in Cincinnati, later moving to Indianapolis, where he practiced.
After the Civil War, during which Harrison served as colonel of the 70th Volunteer Infantry, he enhanced his reputation as a lawyer. In the 1880s, he served in the U.S. Senate, where he championed American Indians, homesteaders and Civil War veterans. In the presidential election of 1888, he received 100,000 fewer popular votes than President Cleveland but carried the Electoral College 233 to 168.
As President, Harrison was proud of his vigorous foreign policy. The first Pan American Congress met in Washington in 1889, establishing an information center which later became the Pan American Union. At the end of his administration, Harrison submitted a treaty to the Senate to annex Hawaii, but his successor withdrew it. He also signed important appropriation bills for internal improvements, naval expansion and subsidies for steamship lines and the Sherman Anti-Trust Act “to protect trade and commerce against unlawful restraints and monopolies.” This act was the first federal attempt to regulate trusts. He was re-nominated by his party in 1892 but lost to Grover Cleveland, who became the only President in U.S. history to serve two non-consecutive terms in office. A dignified elder statesman, he died in 1901.
Coinage Legislation under President Benjamin Harrison
Act of July 14, 1890 — Directing the purchase of silver bullion and the issue of Treasury notes thereon, and for other purposes
Act of September 26, 1890 — To amend section 3510 of the Revised Statues of the United States and to provide for new designs of authorized devices of United States coins (included new designs for coins to be authorized every 25 years.)
Act of September 26, 1890 — An act to discontinue the coinage of the three-dollar and one-dollar gold pieces and three-cent nickel piece
Act of February 10, 1891 — To prevent counterfeiting or manufacture of dies, tools, or other implements used in counterfeiting, and providing penalties therefore, and providing for the issue of search warrants in certain cases
Act of August 5, 1892 — Authorizing coinage of 5,000,000 souvenir half-dollars for the World’s Columbian Exposition